Webhooks
2 minutes to readWebhooks are a powerful tool that automates integrations between different services, which makes them more responsive and efficient. Discover how you can implement this functionality through Caspio Webhooks to improve communication between your applications and further streamline your business processes.
What are webhooks?
Webhooks are a means for web applications to receive real-time notifications of events, such as new orders or customer sign-ups, without having to constantly check for updates. By sending a message to a designated URL when a specific event occurs, webhooks enable applications to communicate with each other without the need for polling or continuous monitoring. With webhooks, applications process updates only when they are needed.
The following diagrams show the main difference between webhooks and API polling:
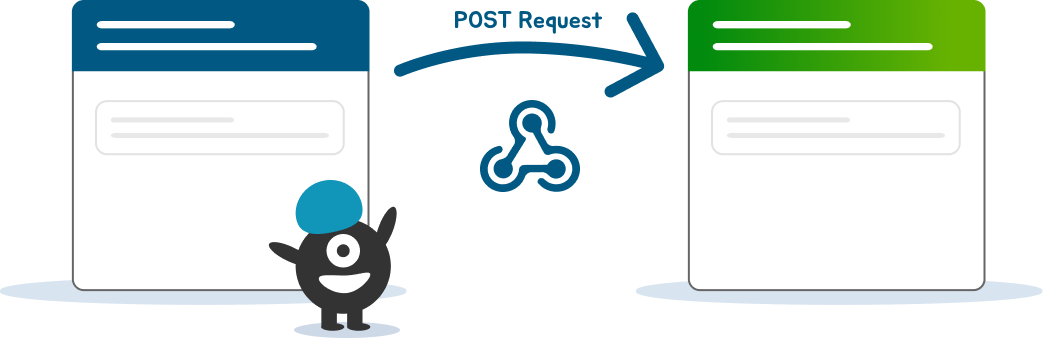
Webhook Communication
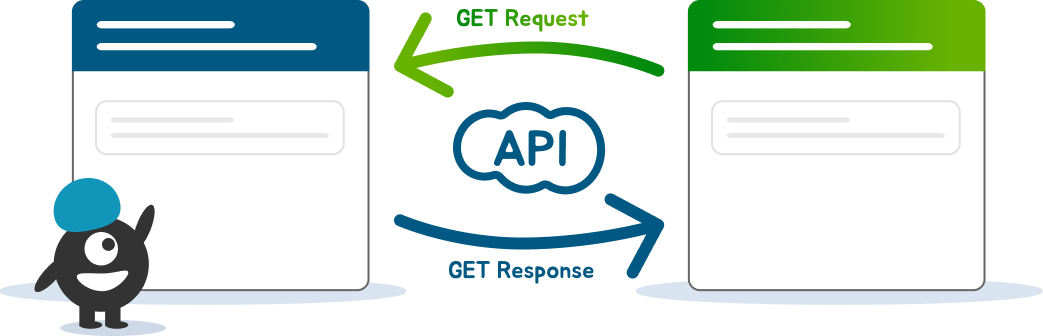
API Communication
How do webhooks work?
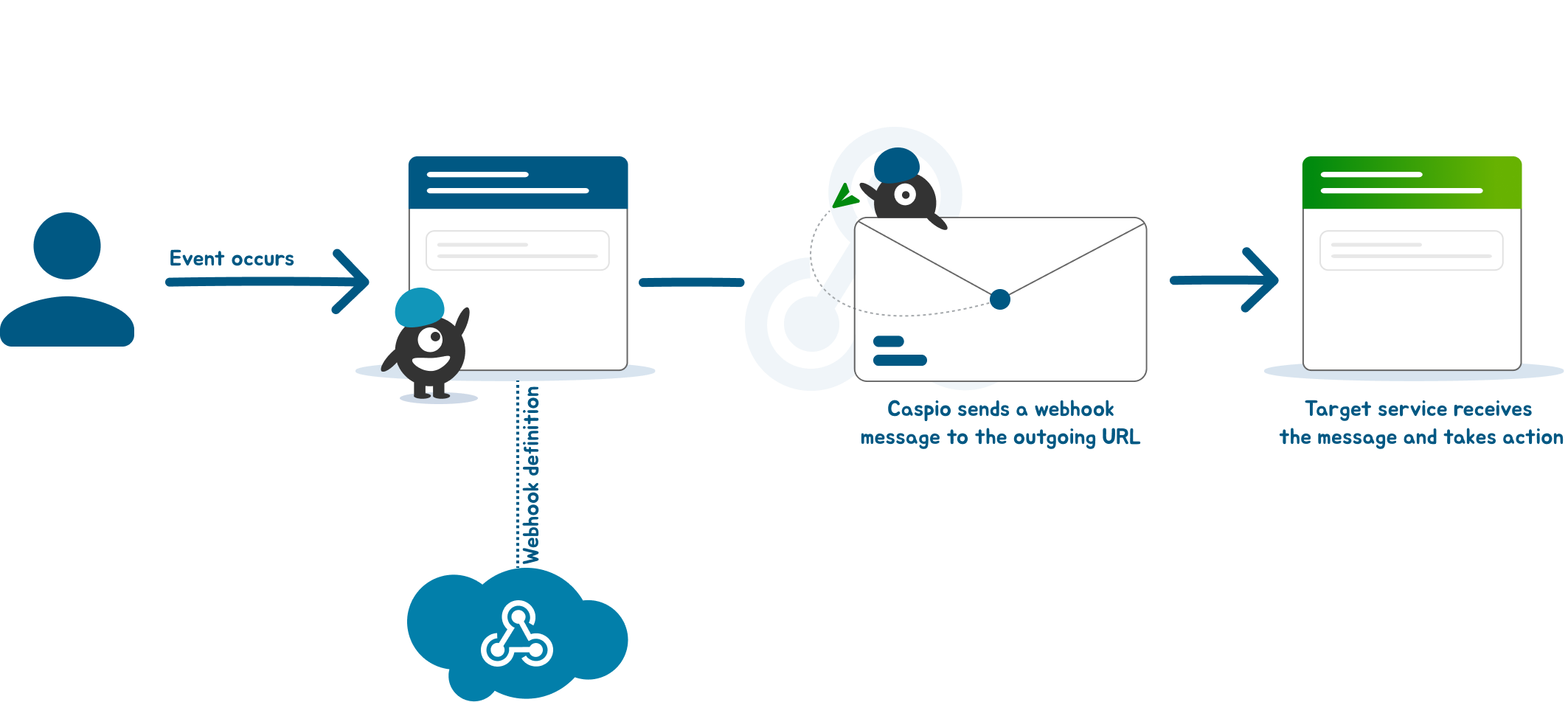
When a webhook is triggered by an event, it sends a message to the target URL in an HTTP POST request. The message includes a payload of data about the event that triggered the webhook, such as the object that was modified, but it might also be limited to a simple notification that an event has occurred.
The payload is usually in JSON format. Once the target service receives the webhook, it can take action based on the payload data.
Why use webhooks?
The advantages of using webhooks over other data transfer methods include:
- Automation: Webhooks are automatically sent out whenever the trigger event occurs in the source system.
- Real-time communication: With webhooks, systems can communicate with each other in real-time, allowing for faster and more efficient data exchange.
- Reduced server load: Webhooks eliminate the need for systems to constantly poll or check for updates, which can save resources and reduce latency.
- Customization and scalability: You can configure webhooks to send only the relevant data, as well as scale them up or down to make sure they process just the right amount of data for your business scenario.
- Flexibility: Webhooks integrate with many other systems and services and you can use them to build custom workflows.
Now that you have learned about the basics of how webhooks work, discover how you can use webhooks in your Caspio applications:

